

They are difficult to reduce and have a lot of compounds that are formed from the reaction with oxygen. Lithophiles: (rock-loving) These consist mainly of silicate minerals which include cations that commonly form oxides. The elements distribute themselves in the earth’s major geochemical reservoirs such as core, mantle, crust, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Goldschmidt that depended on the affinity of elements to form different compounds was one of the most important classification schemes relevant to this aspect of chemistry. This is used in the geochemical analysis. These included very essential elements like oxygen, silicon, iodine, calcium, magnesium, etc.Įlements can be classified into various categories.
In the span of the next 200 years, about 65 more elements were discovered. Gradually elements like arsenic, antimony, bismuth, and zinc also came to be known. They made things like weapons, shelter, fuel, etc with these elements.
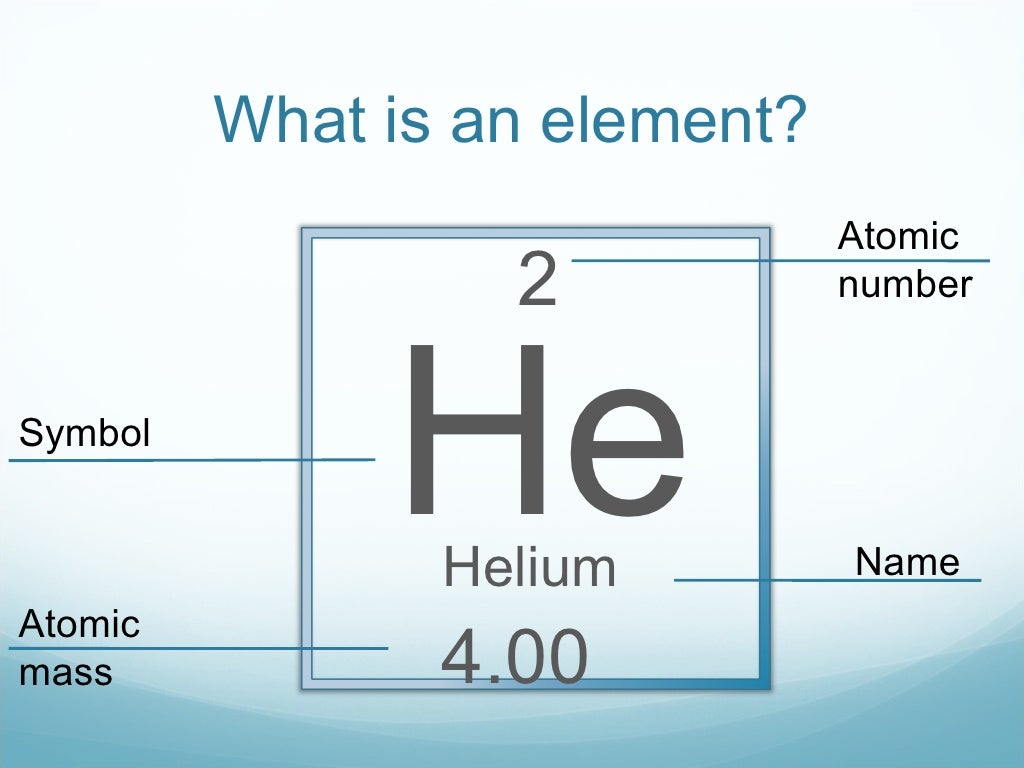
The modern periodic table includes all the elements discovered to date and is arranged mainly based on atomic number.Įlements like carbon, sulfur, iron, tin, lead, copper, mercury, silver, and gold were already known to humans. The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev published the first periodic table in 1869 which was recognized widely, but these consisted of only the elements that were discovered at the time. There are seven rows (with metals on the left and nonmetals on the right) and 18 groups in the periodic table. Periodic Table: The periodic table of elements have the various chemical elements arranged according to the similarity in properties. When the same element has a different mass number (the number of neutrons differs), it is called an isotope. Mass Number: (A) This number represents the number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom. Each element has a unique atomic number that helps us to also identify them when we discover such elements. The nucleus of the atom is made up of protons and neutrons.Ītomic Number: (Z) This is the number of protons that are present in the nucleus of an atom. All atoms are composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons which is bound to the atom’s nucleus. These atoms are very small (around 100 picometers). All solids, liquids, gas, and plasma (a special type of state of matter) is made from neutral or ionized atoms. It has absolutely zero electric charges and mass is the same as that of a proton.Ītoms: This is the smallest unit of matter, it consists of protons, electrons, and neutrons. Neutron: It is a neutral subatomic particle that is present in all atomic nucleus except hydrogen atoms. It carries a negative charge of 1.60217 x 10 -19 coulomb (which is the basic unit of electric charge) Proton: It is a subatomic (contained inside the atom) particle that has a positive charge which is equal in size to an electron and has a mass that is 1836 times the mass of an electron.Įlectron: This is a negatively charged subatomic particle which is the most stable and lightest subatomic particle known. Since elements are made up of atoms, let us first see some basic terms that you will need to know to understand elements. There are around 118 known elements to date. The number of protons in the nuclei is unique for each element and is known as its atomic number. It has a set number of protons in it and changing the number of protons of an element changes the type of element entirely. Element definition in chemistry is “Any pure substance that is made entirely of one type of atom and cannot be broken by chemical means”.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
